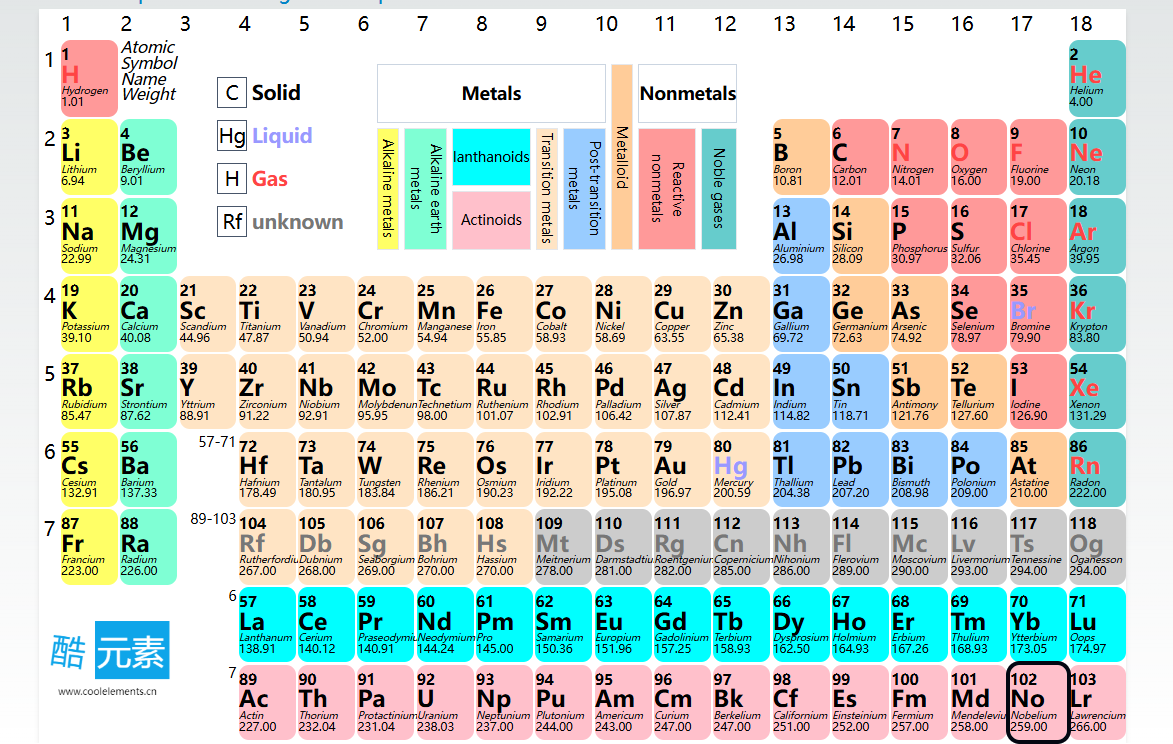
The periodic table is the cornerstone of chemistry, organizing all known elements in an orderly fashion based on their properties and structure. Understanding its organization not only helps you memorize elements but also reveals the relationships and patterns between them.
The Core of the Periodic Table: Atomic Number
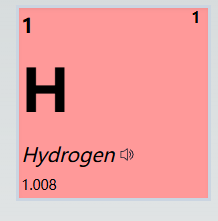
Each element's position in the periodic table is determined by its atomic number, which represents the number of protons in the nucleus. For example, hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, indicating it possesses one proton.
Periods and Groups: The Logic of Element Arrangement
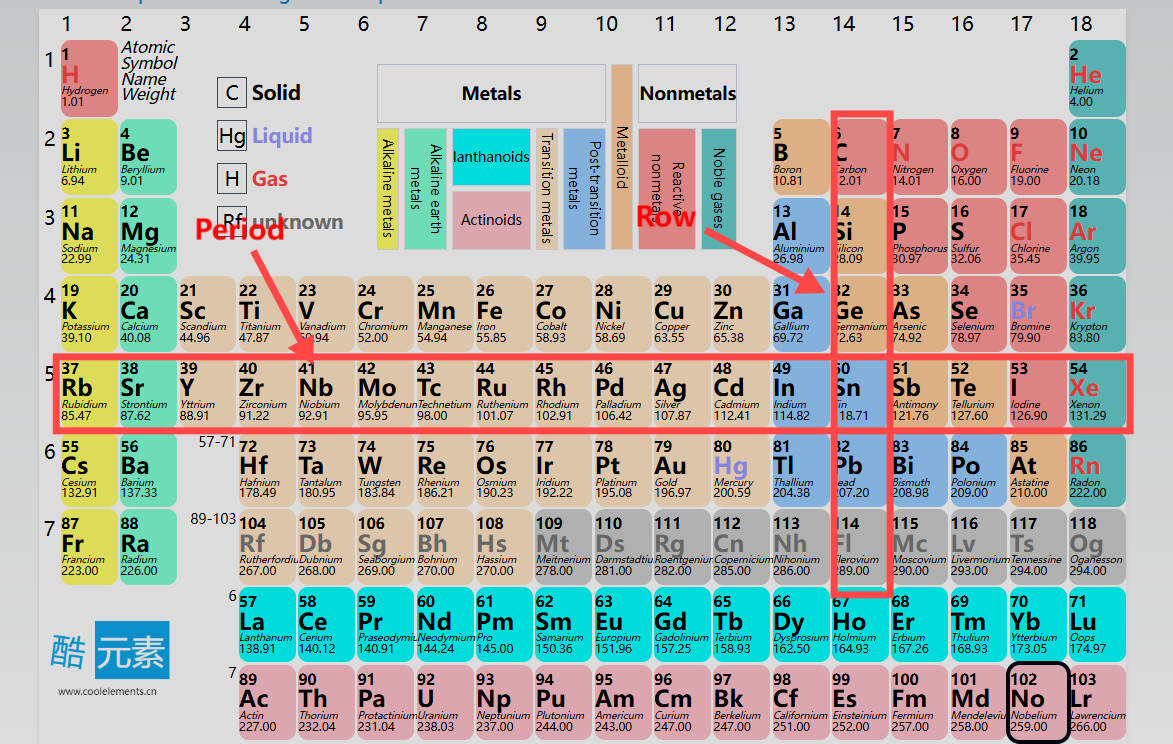
Periods (Rows): The periodic table consists of 7 periods, each corresponding to an increase in the number of electron shells. For instance, elements in the first period have one electron shell, while those in the second period have two, and so on.
Groups (Columns): Elements are divided into 18 groups, with elements in the same group sharing similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons. For example, alkali metals (Group 1) are highly reactive with other elements because they have only one valence electron.
Block Division: Revealing Electron Configuration
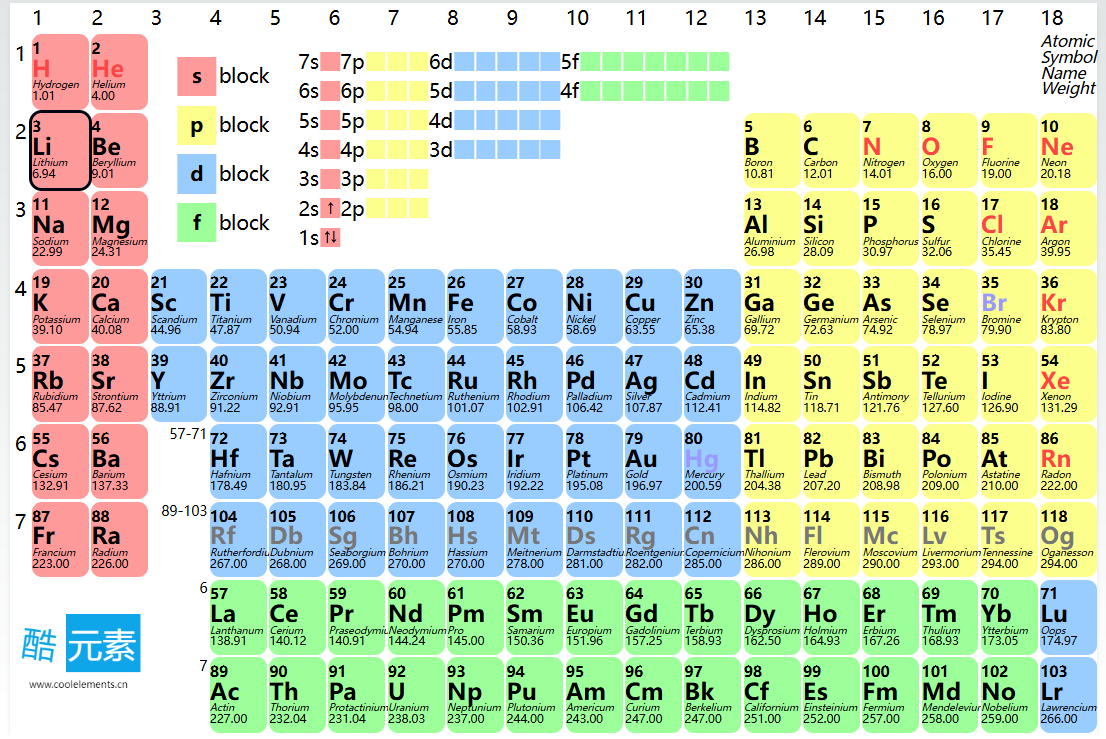
The periodic table can also be divided into four blocks based on electron configuration:
s-Block: Includes Group 1 and 2 elements, where the outermost electrons fill the s-orbital.
p-Block: Includes Groups 13 to 18, where the outermost electrons fill the p-orbital.
d-Block: Includes transition metals, where the outermost electrons fill the d-orbital.
f-Block: Includes lanthanides and actinides, where the outermost electrons fill the f-orbital.
The Significance of the Periodic Table
The periodic table is more than just a list of elements; it is a blueprint that reveals the relationships between elements. By understanding its organization, we can:
Predict Element Properties: An element's position in the periodic table can reveal its chemical properties, such as reactivity and electronegativity.
Discover New Elements: The periodic table provides a theoretical foundation for predicting and discovering new elements.
Understand Chemical Reactions: An element's position in the periodic table helps us understand the principles and patterns of chemical reactions.